Uterine fibroids are a common health concern for many women, particularly those of childbearing age. These noncancerous growths in the uterus can vary in size, location, and number, and their presence often raises questions about their impact on fertility. For women who are planning to conceive, understanding how uterine fibroids might influence their ability to get pregnant is crucial. This article explores the relationship between uterine fibroids and fertility, providing a detailed overview of the types of fibroids, their symptoms, and how they might affect pregnancy.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are benign tumors that originate in the smooth muscle tissue of the uterus. They are the most common type of pelvic tumor in women, with studies suggesting that up to 70-80% of women will develop fibroids at some point in their lives. Despite their prevalence, the exact cause of fibroids remains unclear. However, factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, and growth factors like insulin-like growth factor have been implicated in their development.
Fibroids can range in size from tiny seedlings, undetectable by the human eye, to large masses that can distort and enlarge the uterus. The number of fibroids can also vary; some women may have a single fibroid, while others may have multiple fibroids of varying sizes.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids are classified based on their location within the uterus, and this classification can influence how they affect fertility:
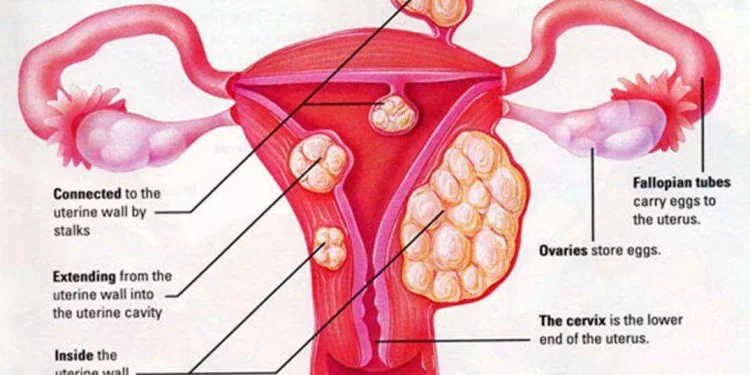
Subserosal Fibroids: These grow on the outer surface of the uterus, extending into the pelvic cavity. They typically do not interfere with the uterine cavity, but large subserosal fibroids can cause discomfort, pressure symptoms, and may indirectly affect fertility by altering the shape and size of the uterus.
Intramural Fibroids: These are located within the muscular wall of the uterus. Intramural fibroids are the most common type and can cause the uterus to enlarge. Their impact on fertility is more significant when they distort the uterine cavity or obstruct the fallopian tubes.
Submucosal Fibroids: These fibroids grow just beneath the lining of the uterine cavity and can protrude into the cavity itself. Submucosal fibroids are the least common but have the greatest potential to interfere with fertility. They can distort the uterine cavity, interfere with implantation, and increase the risk of miscarriage.
Pedunculated Fibroids: These are attached to the uterus by a thin stalk, and can be subserosal or submucosal. Pedunculated fibroids can sometimes twist on their stalks, causing severe pain, but they are less likely to impact fertility unless they grow large.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Many women with fibroids experience no symptoms and may not even be aware of their presence. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include:
Heavy menstrual bleeding: This is the most common symptom, and it can lead to anemia if left untreated.
Pelvic pain or pressure: Large fibroids can cause a feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen or even pain.
Frequent urination: If fibroids press on the bladder, they can cause a need to urinate frequently.
Constipation: Fibroids that press on the rectum can cause difficulty with bowel movements.
Pain during intercourse: Depending on the location of the fibroids, intercourse can become painful.
Lower back pain: This can occur if fibroids press on the muscles and nerves of the lower back.
It’s important to note that the severity of symptoms does not necessarily correlate with the size or number of fibroids. Small fibroids can cause significant symptoms, while large fibroids may remain asymptomatic.
How Uterine Fibroids Can Affect Fertility
The relationship between uterine fibroids and fertility is complex and not fully understood. While many women with fibroids can conceive and carry a pregnancy to term without any issues, fibroids can sometimes affect fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
Impact on Ovulation and Egg Quality
Most fibroids do not interfere with ovulation. However, large intramural or subserosal fibroids that distort the uterus can affect the blood supply to the ovaries, potentially impacting ovulation. There is limited evidence to suggest that fibroids might reduce egg quality, but this is not well-established.
Distortion of the Uterine Cavity
Submucosal fibroids are the most likely to interfere with fertility because they distort the uterine cavity. This distortion can prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg or increase the likelihood of a miscarriage. Even small submucosal fibroids can have a significant impact on fertility by creating an inhospitable environment for embryo implantation.
Obstruction of the Fallopian Tubes
Large fibroids, particularly those located in the isthmus or cornual regions of the uterus, can obstruct the fallopian tubes. This obstruction can prevent sperm from reaching the egg or block the passage of the fertilized egg to the uterus, leading to infertility or ectopic pregnancy.
Changes in the Endometrium
The endometrium is the lining of the uterus where a fertilized egg implants. Fibroids, especially submucosal types, can alter the normal structure of the endometrium, making it difficult for the embryo to implant successfully. Even if implantation occurs, the altered environment may not support the pregnancy, leading to early miscarriage.
Impact on Blood Flow
Fibroids can interfere with the blood flow to the uterine lining, which is critical for supporting a pregnancy. If the blood flow is compromised, the chances of a successful implantation and pregnancy may decrease.
Inflammatory Response
Fibroids can trigger an inflammatory response in the uterus, leading to an environment that is not conducive to pregnancy. Chronic inflammation can affect the implantation process and increase the risk of pregnancy loss.
Hormonal Imbalance
Although fibroids themselves are hormone-sensitive, particularly to estrogen and progesterone, they can contribute to hormonal imbalances that may impact fertility. For example, fibroids can lead to irregular menstrual cycles or anovulatory cycles (cycles where no ovulation occurs), both of which can reduce the chances of conception.
see also: Uterine Fibroids and Fertility: What You Need to Know
Pregnancy Complications Associated with Uterine Fibroids
Even if a woman with fibroids successfully conceives, fibroids can still cause complications during pregnancy. These complications include:
Increased Risk of Miscarriage
Women with fibroids, particularly submucosal fibroids, have a higher risk of miscarriage. This risk is due to the factors mentioned earlier, such as distorted uterine cavity, altered endometrium, and compromised blood flow.
Preterm Birth
Fibroids can increase the risk of preterm birth. This may be due to the space-occupying nature of fibroids, which can cause the uterus to contract prematurely.
Placental Problems
Fibroids can interfere with the normal implantation of the placenta, leading to conditions such as placenta previa (where the placenta covers the cervix) or placental abruption (where the placenta detaches from the uterine wall before delivery). These conditions can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby.
Fetal Growth Restriction
Large fibroids can limit the space available for the growing fetus, leading to intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). Babies born with IUGR are at a higher risk of health problems, both at birth and later in life.
Labor Complications
Fibroids can interfere with normal labor, leading to prolonged labor, abnormal labor positions, or even the need for a cesarean section (C-section). Additionally, fibroids can increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage (excessive bleeding after childbirth).
Pain During Pregnancy
As fibroids grow, they can outgrow their blood supply, leading to a condition called “red degeneration,” which can cause severe pain during pregnancy. While this pain usually resolves on its own, it can be distressing and may require hospitalization.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Uterine Fibroids
If you suspect that you have fibroids or are experiencing symptoms that could be related to fibroids, it is important to seek medical advice. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of a physical examination, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI, and sometimes a hysteroscopy, where a camera is inserted into the uterus to directly visualize the fibroids.
Treatment options for fibroids vary depending on the size, location, symptoms, and the desire for future fertility. Here are some common treatment approaches:
Watchful Waiting
If the fibroids are small, asymptomatic, and not interfering with fertility, a watchful waiting approach may be recommended. This involves regular monitoring to ensure that the fibroids are not growing or causing problems.
Medications
Several medications can be used to manage the symptoms of fibroids, but they do not eliminate fibroids. These include:
Hormonal Therapies: These can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce heavy bleeding, and shrink fibroids temporarily. Examples include gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, progestins, and oral contraceptives.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These can help manage pain associated with fibroids.
Tranexamic Acid: This is used to reduce heavy menstrual bleeding.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For women who are experiencing symptoms or infertility related to fibroids but want to preserve their uterus, several minimally invasive procedures are available:
Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): This procedure involves blocking the blood supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink. It is effective for reducing symptoms but is generally not recommended for women who wish to become pregnant.
Myomectomy: This surgical procedure involves removing the fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. Myomectomy is the preferred option for women who want to preserve their fertility. It can be performed through various approaches, including hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, or an open abdominal surgery, depending on the size and location of the fibroids.
Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Surgery (MRgFUS): This is a newer, noninvasive technique that uses focused ultrasound waves to destroy fibroid tissue. It is a promising option for women with symptomatic fibroids who wish to avoid surgery, though its long-term effects on fertility are still being studied.
Surgical Options
In more severe cases, where fibroids are causing significant symptoms or are large and numerous, surgery may be recommended:
Hysterectomy: This is the complete removal of the uterus and is considered the definitive treatment for fibroids. It is recommended for women who have completed their families or do not wish to preserve fertility.
Endometrial Ablation: This procedure destroys the lining of the uterus to reduce heavy bleeding. It is not suitable for women who wish to have children in the future.
Fertility Preservation and Planning
For women with fibroids who are planning to conceive, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a plan that optimizes fertility and minimizes risks. Here are some considerations:
Preconception Counseling
Before attempting to conceive, women with fibroids should undergo a thorough evaluation to assess the size, number, and location of fibroids. This evaluation can help determine whether treatment is needed before trying to get pregnant.
Timing of Pregnancy
If fibroids are diagnosed during the early reproductive years, a healthcare provider may recommend trying to conceive sooner rather than later. Fibroids can grow over time, potentially leading to more complications with age.
Fertility Treatments
For women with fibroids who have difficulty conceiving, fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be considered. In some cases, removing fibroids before IVF can improve the chances of success.
Monitoring During Pregnancy
Women with fibroids who become pregnant should be closely monitored throughout their pregnancy. Regular ultrasounds can help track the growth of fibroids and assess any potential impact on the pregnancy.
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids can pose challenges to fertility and pregnancy, but many women with fibroids are able to conceive and have successful pregnancies. The impact of fibroids on fertility depends on several factors, including the size, location, and number of fibroids, as well as the overall health and reproductive history of the woman. With proper medical care, many of the risks associated with fibroids can be managed, allowing women to achieve their reproductive goals.
If you have fibroids and are concerned about your fertility, it is essential to seek advice from a healthcare provider who can offer personalized guidance based on your individual circumstances. By understanding the nature of fibroids and the available treatment options, you can make informed decisions that support your reproductive health and future family plans.
Related topics: